
Overview of NPS
National Pension System



The National Pension System (NPS) is a pension scheme launched and promoted by the Govt. of India. The scheme allows citizens to undertake retirement planning by investing periodically during their working life and building a corpus for a financially secured retired life. It is a market-linked defined contribution pension scheme.
NPS is regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA). The scheme is mandatory for Central Government employees (except armed forces) who have joined service and on or after 01 Jan 2004 and for employees of those State Governments who have adopted NPS .
Indian citizens (including NRIs and OCIs) aged between18 and 70 years can open an NPS Account. Corporates (private and public sector) both in the private and public sectors, can introduce NPS as an employee retirement benefit scheme.
Features & Benefits of NPS
Regular pension on retirement
Low-cost pension scheme
Additional tax benefits on investment
Withdrawals for emergencies
Risk spread across asset classes
Portability across jobs and locations
Tax-free withdrawals on exit
Why join NPS early?
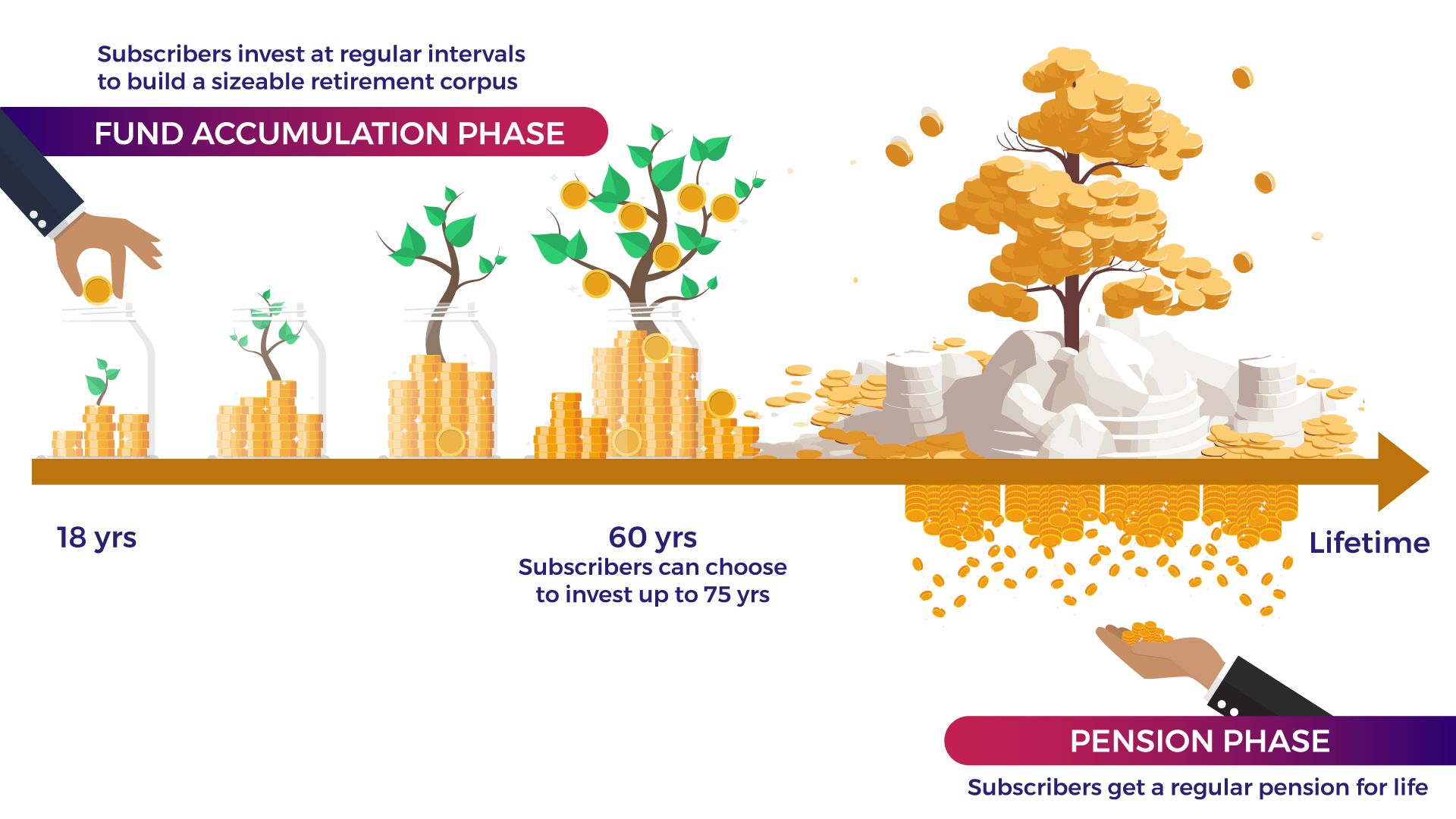
How Does NPS Work?
Intermediaries under NPS Ecosystem
Under NPS ecosystem, there are several intermediaries that are authorised by the PFRDA to provide different services related to NPS.
Currently, there are three CRAs in NPS:
